|
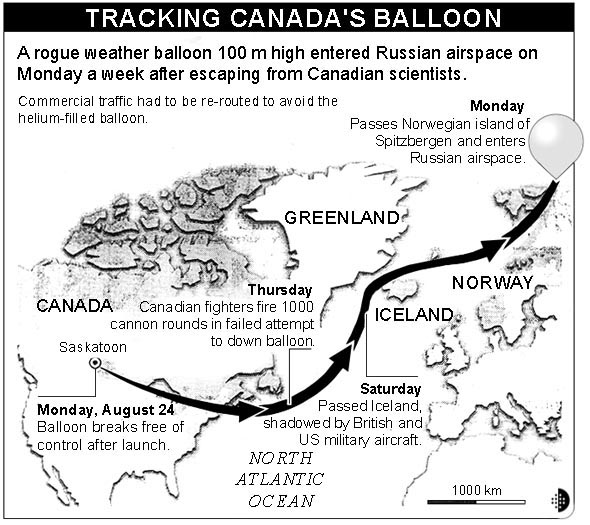
A runaway 25-storey balloon is thought to have finally come down
A huge runaway Canadian weather balloon which stayed aloft for more than a week, forcing disruptions in transatlantic flights is believed to have finally come down in the Arctic, say its owners. Source: Unknown. |
| a) |
Where was the balloon when it was attacked by Canadian fighter planes?
|
| b) |
What effect did the runaway balloon have on aircraft flying across the North Atlantic Ocean?
|
| c) |
What reason did the Canadian Lieutenant give for the failure of the CF-18 fighter pilots to destroy the balloon?
|
| d) |
Where was the balloon located on Sunday 30 August?
|
| e) |
What is the size of the balloon's surface area compared with?
_________________________________________________ |
| f) |
Exactly where was the balloon launched from?
_________________________________________________ |
| g) |
What does "rogue" mean, as used in this article?
_________________________________________________ |
| h) |
What word could replace "shadowed" without changing the meaning in the statement … "shadowed by British and US military aircraft"?
_________________________________________________ |
| i) |
What was the balloon's mission?
_________________________________________________ |
| j) |
Where did the balloon crash eventually? _________________________________________________ |