Circuit investigations
| What is a circuit? | ||||||
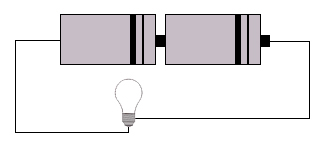
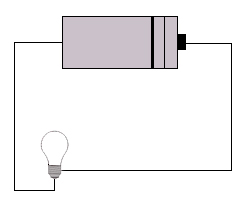
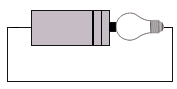
| a) | i) | Using the equipment you have, test each of the following circuits. Put a tick over it if it works, or a cross if it doesn't. | ||||
1) 2) 2)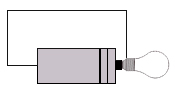 3) 3) |
||||||
4) 5) 5)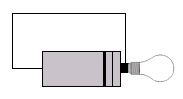 6) 6)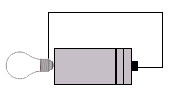 |
||||||
| ii) |
Why do some of the circuits work, while others do not?
|
|||||
| b) |
Now make up these two circuits.
|
|||||
| i) |
What did you find out?
|
|||||
| ii) |
Explain why this happened.
|
|||||
| c) |
Make up these two circuits and explain your results.
|
|||||
|
|
||||||