Candle combos
This task is about possible outcomes, tree diagrams and probability.
|
Lynne had some candles in a box.
The height of each one was either tall or short.
The colour of each one was either yellow or red.
The probability of the height being:
The probability of the colour being:
|
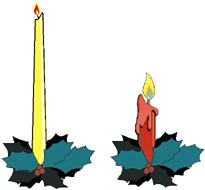 |
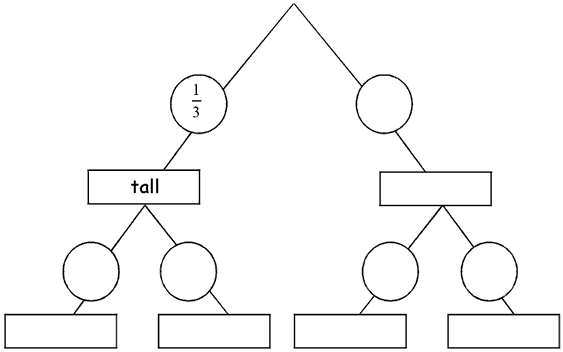
The tree diagram below illustrates the probabilities of all the different combinations of height and colour of the candles.
| a) |
Complete the tree diagram by filling in all the blank boxes and circles with the correct word or probability.
One probability and one word have been written in for you.
|
|
| b) |
A candle is chosen without looking. What is the probability that the candle is ...
|
|
|
i) ii) |
tall and yellow? __________
short and red? __________
|
|



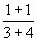 = 2/7
= 2/7 = 5/7
= 5/7