NMSSA Science Toolkit - Assessment 2
This is an assessment of your learning in science.
In this test there are four different types of questions for you to answer. You might need to:
1. Click on one or more answers to select them.
2. Choose a word from a drop down menu to complete a sentence.
3. Draw and/or label diagrams.
2. Choose a word from a drop down menu to complete a sentence.
3. Draw and/or label diagrams.
4. Write a response to a question.
When you have answered a question click on the Next button  . To go back to a question you have already attempted click on the grey back arrow button.
. To go back to a question you have already attempted click on the grey back arrow button. 
You may need to scroll down the page to read all the information.
There are 36 questions in this test. It should take you about 45 minutes to complete. Try to answer all the questions.
Static electricity
|
Read the information below then click on the Next button to answer some questions.
Students in room 6 were investigating static electricity. They rubbed a balloon on different materials and held it above their hair. When their hair stood up, their teacher said they had made static electricity. Here are the results of their investigation.
|
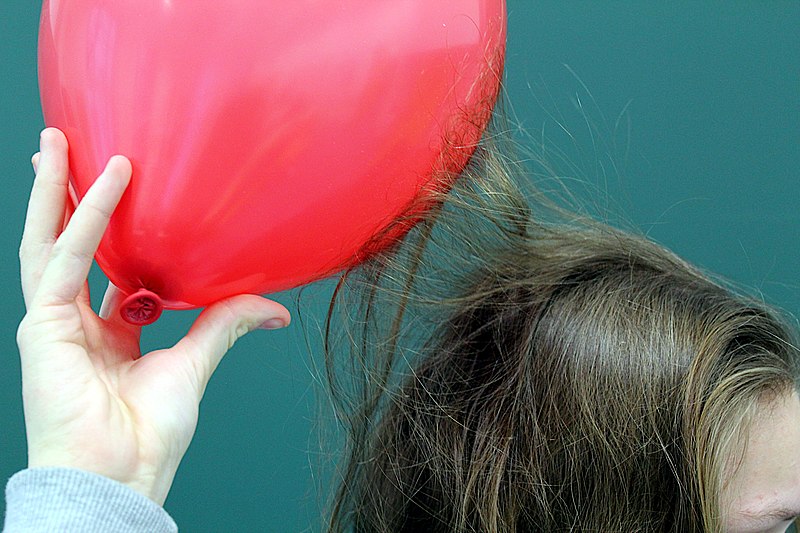

© MikeRun | Wikipedia, CC-BY SA 4.0
|
Room 6 investigation
Materials tested for static electricity
| Materials | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cotton | N | N | N | Y | N |
| rayon | N | N | N | Y | Y |
| polyester | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| wool | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| silk | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
Key:
| Y | Hair stood up | Static electricity was made |
| N | Hair did not stand up | Static electricity was not made |
Kea and kākā
Living things change over time. This helps them survive when the conditions of the places they live in change.
Kea and kākā look similar. Scientists think that a long time ago they had the same ancestor.
|
Kea
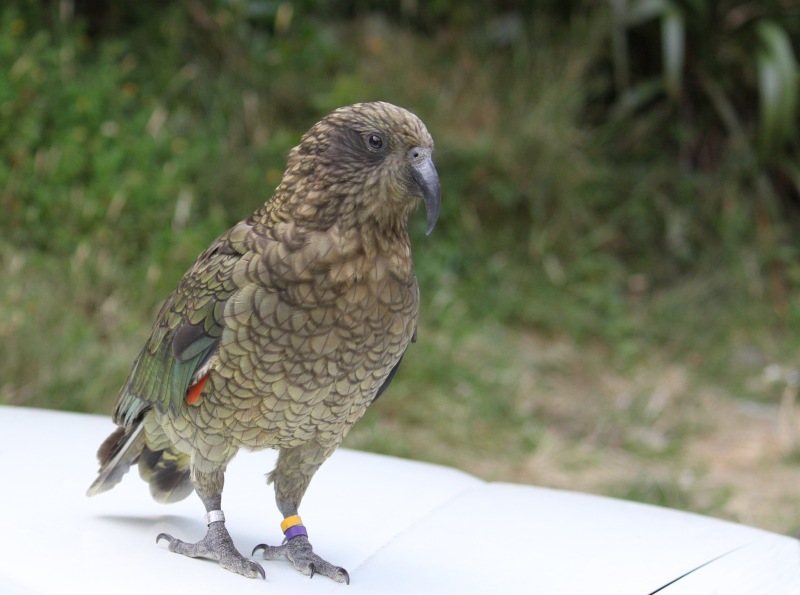

© J.Fisher | PhotoKete
|
Kākā
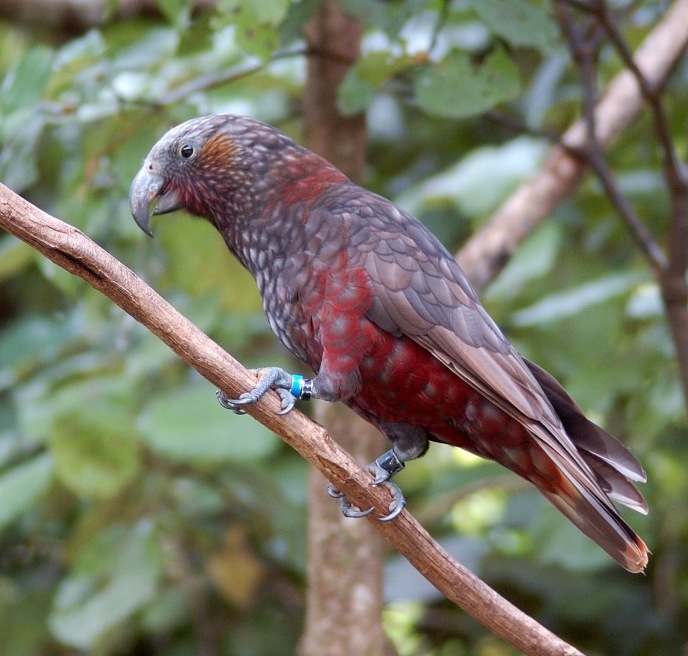

© Rosino | Flickr, CC-BY 2.0
|

