Heating octane
This task is about changing states of matter: solid, liquid and gas.
A heating curve is a graph that represents the stages of matter that a substance changes into as heat is added to it. The flat lines on the curve mark where the stages of matter change. The temperature is constant at these transition points.
| This is the heating curve of octane (the main component in petrol). |
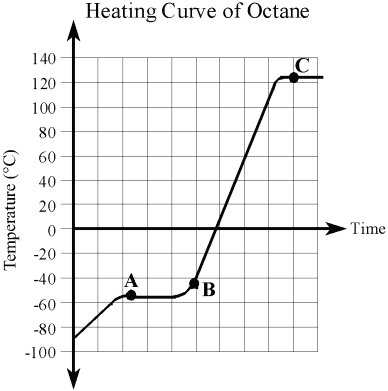 |
| a) | i) |
What is the temperature of the octane at the start of the investigation? __________°C
|
| ii) |
Is the state of the octane a solid, liquid, or gas at the start of the investigation?
_______________
|
|
| b) |
At what temperature does the octane begin melting? __________°C
|
|
| c) |
At what temperature does the octane begin boiling? __________°C
|
|
| d) |
What two states would you observe at point A?
1. ____________________ 2. ____________________
|
|
| e) |
What state would you observe at point B? ____________________
|
|
| f) |
What two states would you observe at point C?
1. ____________________ 2. ____________________
|
|
| g) |
Describe what is happening to the particles when the octane becomes liquid. The particles:
|
|
| h) |
Describe what is happening to the particles when the octane is rapidly boiling. The particles:
|
|

