Insect or spider?
This task is about using evidence to decide if six animals are insects or spiders.
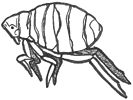
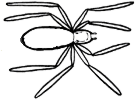
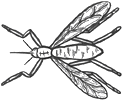
Ms Norman’s Year 6 class is studying spiders. The class has been asked to find a spider in the playground and draw it. Some children got muddled and drew insects. Use the insect and spider charts below to decide which drawings are of spiders and which are of insects. Give as many reasons as you can for your answers.
|
Features of all insects
3 body parts
6 legs
antennae
|
Features of all spiders
2 body parts
8 legs
spinnerets for making webs
|